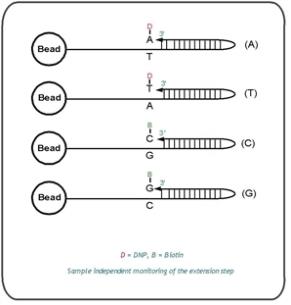
Sample-Independent Controls
Sample-independent controls evaluate the performance of specific steps in the process flow.
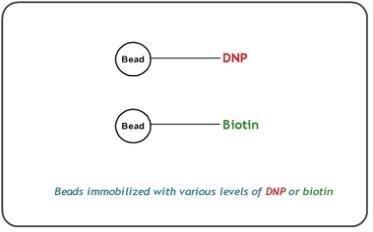
Staining controls are used to examine the efficiency of the staining step in both the red and green channels. Staining controls have various levels of dinitrophenyl (DNP) or biotin attached to the beads. These controls are independent of the hybridization and extension step. Various levels of DNP and biotin monitor the sensitivity and efficiency of the staining step. Both red and green channels can be evaluated using the staining controls.
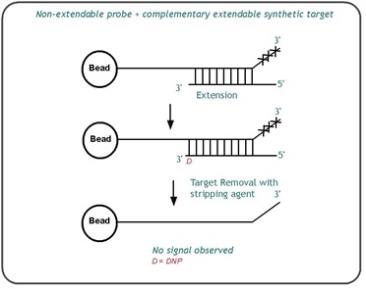
Target removal controls test the efficiency of the stripping step after the extension reaction. In contrast to allele-specific extension, the control oligos are extended using the probe sequence as template. This process generates labeled targets. The probe sequences are designed such that extension from the probe does not occur.
All target removal controls can result in low signal compared to the hybridization controls, indicating that the targets were removed efficiently after extension. The target removal controls are present in the Hybridization Buffers (RA1, IBX). Performance of target removal controls can only be monitored in the red channel.
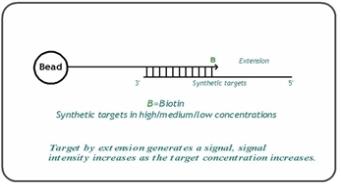
The hybridization controls test the overall performance of the entire assay using synthetic targets instead of amplified DNA. These synthetic targets complement the sequence on the array perfectly, allowing the probe to extend on the synthetic target as template.
The synthetic targets are present in the Hybridization Buffer (RA1, IBX) at three levels. They monitor the response from high concentration (5 pM), medium concentration (1 pM), and low concentration (0.2 pM) targets. All bead type IDs can result in signal with various intensities, corresponding to the concentrations of the initial synthetic targets. Performance of hybridization controls can only be monitored in the green channel.