Dilute Libraries to the Starting Concentration
This step dilutes exome-enriched pooled libraries to the starting concentration for your sequencing system and is the first step in a serial dilution. After diluting to the starting concentration, exome-enriched pooled libraries are ready to be denatured and diluted to the final loading concentration.
Illumina recommends setting up a paired-end run with 101 cycles per read (2 × 101) and 10 cycles per Index Read. If you would like additional overlapped reads or additional raw coverage, you can sequence up to 2 × 126 or 2 × 151, but it is not required.
| 1. | Calculate the molarity value of the library or pooled libraries using the following formula. |
| • | For libraries qualified on a Bioanalyzer, use the average size obtained for the library. |
| • | For other qualification methods, use 350 bp as the average library size. |
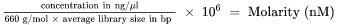
| 2. | Using the molarity value, calculate the volumes of RSB and pooled library needed to dilute libraries to the starting concentration for your system. |
|
Sequencing System |
Starting Concentration (nM) |
Final Loading Concentration (pM) |
|---|---|---|
|
HiSeq 4000 and HiSeq 3000 Systems |
2–3 |
150–200 |
|
NextSeq 550 and NextSeq 500 Systems |
2 |
1.4–1.5 |
|
NextSeq 1000/2000 System |
2 |
1000 |
|
NovaSeq 6000 System (standard workflow) |
2 |
175–185 |
|
NovaSeq X System |
2 |
150 |
| 3. | Dilute libraries using RSB as follows. |
| • | Libraries quantified as a pool—Dilute the pool to the starting concentration for your system. |
| • | Libraries quantified individually—Dilute each library to the starting concentration for your system. Add 10 µl from each diluted library to a tube to create a multiplexed library pool. |
| 4. | Follow the denature and dilute instructions for your system to dilute to the final loading concentration. |
The final loading concentrations are a starting point and general guideline. Optimize concentrations for your workflow and quantification method over subsequent sequencing runs or by flow cell titration.
