Dilute Libraries to the Starting Concentration
This step dilutes libraries to the starting concentration for your sequencing system, and is the first step in a serial dilution. After diluting to the starting concentration, libraries are ready to be denatured and diluted to the final loading concentration.
For sequencing, Illumina recommends
| 1. | Calculate the molarity value of the library or pooled libraries |
| • | For libraries qualified on a bioanalyzer, use the average size obtained for the library. |
| • | For all other qualification methods, use 350 bp as the average library size. |
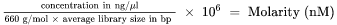
| 2. | Using the molarity value, calculate the volumes of RSB and library needed to dilute libraries to the starting concentration |
|
Sequencing System |
Starting Concentration (nM) |
Final Loading Concentration (pM) |
|---|---|---|
|
iSeq 100 |
2 |
100 |
|
MiniSeq |
2 |
2 |
|
MiSeq (v3 reagents) |
4 |
10–12 |
|
NextSeq 550 |
2 |
1.4–1.5 |
|
NextSeq 1000/2000 |
2 |
1000 |
| 3. | Dilute libraries using RSB: |
| • | Libraries quantified as a multiplexed library pool—Dilute the pool to the starting concentration |
Add 10 µl of each diluted library to a tube
| 4. |
|
| • | The final loading concentrations are a starting point and general guideline. Optimize concentrations for your workflow and quantification method over subsequent sequencing runs or by flow cell titration. |
