DRAGEN Fragmentomics
Fragmentomics is the study of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA or circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). DNA molecules are released into the plasma from various tissues and cell types. Fragmentation features, such as fragment sizes and end motifs, of the cell-free DNA contains the characteristics of their tissue of origin. Studies have shown that fragmentation features are distinct between cancer and noncancer cells derived from ctDNA. The use of genome-wide fragment profile of cell-free DNA has proven to be a powerful tool to infer cancer status and their tissue of origin. The DRAGEN fragmentomics component computes three fragmentomics metrics as following.¹
| 1. | Fragment profile |
| 2. | End motif frequency |
| 3. | Window protection score (WPS) |
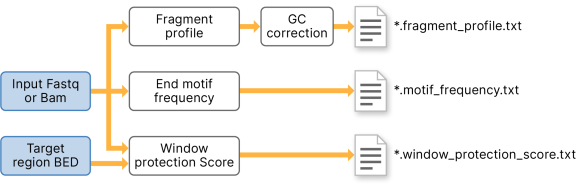
The fragmentomics component works by taking aligned reads from the mapper, calculating per read metrics, and finally tabulating into per-bin or target region metrics. DRAGEN first gets the chromosome sizes from the reference genome. Only autosomes and X, Y chromosomes are considered for fragment profile calculation. The genome is binned with the bin size specified by the user. Each aligned read is processed sequentially. Only reads satisfied with the following criteria are considered:
| • | Mapped |
| • | Mate-mapped |
| • | Not a PCR duplicate |
| • | Primary alignment |
| • | Mapping quality is not less than minimum mapq specified by the user |
Reads that have template length within the short fragment size ranges are counted as short fragment. Reads that have template length within the long fragment size range are counted as long fragment. The fragment profile is calculated as the ratio of short-to-long fragment counts for each genomic bin. Genome-wide short fragment counts, long fragment counts, and their ratio are normalized against the GC bias of each genomic bin using the GC correction module from DRAGEN CNV component.
End motif frequency calculation is enabled when --fragmentomics-end-motif-len is set to positive integers. Unmapped, duplicated, or secondary alignments are excluded for end motif frequency calculation. The first x base pair sequences (x is specified by --fragmentomics-end-motif-len) at the 5' end of the reads is tabulated into a frequency dictionary with keys being the sequences and values being the frequencies. If the first x basepair contains any 'N's, this read will be ignored. After all reads are processed, the frequency table is sorted by the sequences in alphabetic order.
Window protection score (WPS) calculation is enabled when a target region is provided with --fragmentomics-wps-target-file. This file must be a BED format text file with three columns. Each row in the file represents a 120-bp region for which WPS will be calculated. An interval tree will be constructed for the target regions. Then each aligned read is processed sequentially, and unmapped, duplicated, or secondary alignments are excluded. Any read with 5' end falling in a target region increments the read count for the region by one. Forward and reverse reads are counted separately. If a read fully spans the region, the fully-span read count for the region increments by one. After all reads are processed, WPS is calculated for each target region. Two ways of WPS calculation are supported, 1) number of fully spanning rads subtracted by the number of reads with 5' ending in the region. 2) percentage of reads ending in the region of all reads mapped to this region.
DRAGEN Fragmentomics currently supports Tumor-only and Normal-only sequencing data from TSO500/WES/WGS ctDNA assays. The results for Tumor-Normal pair data are undefined because ctDNA data are derived from mixture of tumor and normal DNA. Therefore, users should avoid running Fragmentomics in Tumor-Normal mode.
Required:
Enable the Fragmentomics component:
--enable-fragmentomics
Optional:
--fragmentomics-bin-size Uint. Default 100000
--fragmentomics-num-threads Uint. Default 12
--fragmentomics-min-mapq Uint. Default 30
--fragmentomics-short-fragment-min-size Uint. Default 100
--fragmentomics-short-fragment-max-size Uint. Default 150
--fragmentomics-long-fragment-min-size Uint. Default 151
--fragmentomics-long-fragment-max-size Uint. Default 220
--fragmentomics-num-gc-bins Uint. Default 25
--fragmentomics-gc-enable-smoothing Bool. Default true
--fragmentomics-end-motif-len. Uint. Default 4
--fragmentomics-wps-target-file String
--fragmentomics-exclude-bed String
The target regions file is used only in window protection score calculation. The target regions file is in BED format with three columns.
chr1 2488101 2488120
chr1 2488120 2488174
Users can provide a blocklist of regions to remove reads from fragment profile calculation. For example, low mappability regions. This file is in BED format with three columns.
chr1 1 1000
chr2 1000 2000
dragen \
--ref-dir=$REF \
--fastq-file1 $fastq1 \
--fastq-file2 $fastq2 \
--RGID "test" \
--RGSM "test" \
--enable-map-align true \
--enable-sort false \
--generate-ploidy-vcf false \
--enable-cnv false \
--enable-fragmentomics true \
--fragmentomics-exclude-bed hg19_exclude.bed \
--fragmentomics-bin-size 100000 \
--fragmentomics-num-threads 12 \
--fragmentomics-min-mapq 30 \
--fragmentomics-short-fragment-min-size 100 \
--fragmentomics-short-fragment-max-size 150 \
--fragmentomics-long-fragment-min-size 151 \
--fragmentomics-long-fragment-max-size 220 \
--fragmentomics-num-gc-bins 25 \
--fragmentomics-gc-enable-smoothing true \
--fragmentomics-end-motif-len 4 \
--fragmentomics-wps-target-file hg19.window.bed \
--output-directory $outdir \
--output-file-prefix $outprefix
The system should output the fragment profile file, and optionally the end motif frequency file or WPS file if either or both are enabled.
The fragmment profile file is in the following format:
Chr Start End ShortFragCounts LongFragCounts ShortToLongRatio GCBias ShortFragCountsCorrected LongFragCountsCorrected ShortToLongRatioCorrected
chr1 0 100000 4 7 0.571429 0.424522 3.921048 6.925498 0.572042
chr1 100000 200000 1 2 0.500000 0.436106 0.980262 1.978714 0.500537
chr1 200000 300000 0 2 0.000000 0.391445 0.000000 2.008326 0.000000The end motif frequency file is in the following format:
Motif Frequency
AAAA 111559
AAAC 39204
AAAG 56773
AAAT 68437The WPS file is in the following format:
Chr Start End ForwardCount ReverseCount FullySpanCount WPS TotalCount RatioForward RatioReverse
chr1 2488101 2488120 3 21 314 290 355 0.0084507 0.0591549
chr1 2488101 2488140 3 32 285 250 366 0.00819672 0.0874317
chr1 2488101 2488160 4 41 255 210 376 0.0106383 0.1090431. Y. M. DENNIS LO, DIANA S. C. HAN, PEIYONG JIANG, ROSSA W. K. CHIU. Epigenetics, fragmentomics, and topology of cell-free DNA in liquid biopsies. Science. 2021. DOI: 10.1126/science.aaw3616
